Introduction
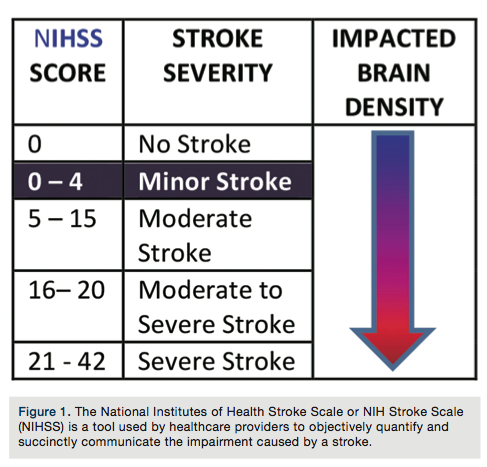
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) is probably the most widely used assessment tool for determining the severity of stroke on neurological examination¹. NIHSS first was developed as a 15-item scale, but then later on it was reduced to 11 items. The scoring scheme starts from 0 (no deficit) to 42 (severe stroke), and as seen in figure-1, research shows a strong correlation between the size of the ischemic lesion on brain imaging and the total score ². Although NIHSS lacks inter-rater reliability, it has become a standard communication tool between clinicians in order to stratify patients based on severity of their symptoms³ .
An example of a patient with a moderate to severe stroke with aphasia and right-sided weakness
NIH Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS) from MDCalc.com on 2/25/2015
** All calculations should be rechecked by clinician prior to use **
RESULT SUMMARY:
19 points out of 42
NIH Stroke Scale
INPUTS:
1A: Level of consciousness —> 1 = Arouses to minor stimulation
1B: Ask month and age —> 2 = Aphasic
1C: ‘Blink eyes’ & ‘squeeze hands’ —> 1 = Performs 1 task
2: Horizontal extraocular movements —> 1 = Partial gaze palsy: corrects with oculocephalic reflex
3: Visual fields —> 1 = Partial hemianopia
4: Facial palsy —> 2 = Partial paralysis (lower face)
5A: Left arm motor drift —> 0 = No drift for 10 seconds
5B: Right arm motor drift —> 3 = No effort against gravity
6A: Left leg motor drift —> 0 = No drift for 5 seconds
6B: Right leg motor drift —> 3 = No effort against gravity
7: Limb Ataxia —> 0 = Does not understand
8: Sensation —> 2 = Complete loss: cannot sense being touched at all
9: Language/aphasia —> 2 = Severe aphasia: fragmentary expression, inference needed, cannot identify materials
10: Dysarthria —> 0 = Intubated/unable to test
11: Extinction/inattention —> 1 = Visual/tactile/auditory/spatial/personal inattention
The NIHSS Booklet and PDF Forms
 Loading…
Loading…
 Loading…
Loading…
Certification
If your hospital does not have a NIHSS learning protocol, or if you are office-based, you can take advantage of the professional learning portals of the heart and stroke association (you need a professional membership).
References:
1. Brott T, Adams HP, Olinger CP, et al. Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: a clinical examination scale. Stroke. 1989;20(7):864-870.
2. Hinkle Janice L. Reliability and Validity of the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale for Neuroscience Nurses. Stroke. 2014;45(3):e32-e34. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.004243
3. Powers DW. Assessment of the stroke patient using the NIH stroke scale. Emerg Med Serv. 2001;30(6):52-56. 4. NIH Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS). MDCalc. https://www.mdcalc.com/nih-stroke-scale-score-nihss. Accessed June 5, 2019.
Rémy Cohan